いろいろ —â“€ƒAƒXƒpƒ‰ ƒŒƒVƒs ‚¨•Ù“– 230180
I I N T R O D U C T I O N A P U R P O S E O F T H I S R E Q U E S T F O R P R O P O S A L S R e g i o n I X E d u c a t i o n C o o p e r a t i v e ( R E C I XWe can check that PTP= I n by a lengthy computation, or more simply, notice that (P TP) ij = 0 B @ uT 1 u 2 uT 3 1 C A u 1 u 2 u 3 = 0 B @ 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 C A We are using orthonormality of the u i for the matrix multiplication above Orthonormal Change of Basis and Diagonal MatricesZ ( } o W Z W l l o Ì } } } X P v Ç X } u l µ o lZW µ Ç ó íy, ì Yh ^d/KE l E^t Z^ í X d Z } µ u v v Z î v Á ó ì u l Z } µ o v o o v Z v o o o

重生明珠 七和香
—â"€ƒAƒXƒpƒ‰ ƒŒƒVƒs ‚¨•Ù"–
—â"€ƒAƒXƒpƒ‰ ƒŒƒVƒs ‚¨•Ù"–-A n d t h o s e e x p e c t a t i o n s a r e g e n e r a l l y u n observable As reviewed briefly in the next section, past r e s e a r c h e r s h a v e t r i e d t o m e a s u r e s u c h e x p e c t a t i o n s i n s e v e r a l ways, none of which is completely c o n v i n c i n gIf you reside in the US territories, please call Goldman Sachs at with questions about accessing this offer or applying for Apple Card This offer cannot be combined with the Apple Employee Purchase Plan or business loyalty pricing Availability of instore promotion offerings may be limited by Apple Store location closures as a



Http Www Idfpr Com Renewals Apply Forms Md Vrp Pdf
S E W } P u D o } v í X ^ µ v u µ l ^ s í ì ì } ^ s í ì í v Z ( u EKs X D ^KE 'Z Z Yh/Z D Ed ^ Yh E } µ D ^KECO V I D19 sympt oms and when t hey began I f you need support or help call your healt hcare provider I f y o u w e r e e x p o s e d to C O V I D 1 9 a n d a r e F U L L Y V A C C I N A T E D T a ke st e p s t o p ro t e ct yo u rse l f a n d o t h e rs G et t est ed 35 days af t er t he day youI came to the US from China with a bachelor's degree in Physics from ShanXi Normal University I received my Master's Degree in Computer Science from University of Nevada, Reno in 1997 I received my PhD degree in Computer Science and Engineering from University of NevadaReno in 14 under the supervision of Dr Sergiu Dascalu
Y= utsin 1 2 gt 2 y= xtan g 2u2 cos2 x2 T= usin g;P R I O R I T Y D a t e 0 2 / 2 1 / 2 0 0 7De–nition 297 Let V denote a vector space and S = fu 1;u 2;;u nga subset of V S is called a basis for V if the following is true 1 S spans V 2 S is linearly independent This de–nition tells us that a basis has to contain enough vectors to generate the entire vector space But it does not contain too many In other words, if we
Title Microsoft Word January 17 Board Meeting Materials Author Kristi Created Date PMOEE = A x P x Q Operating equipment effectiveness (OEE) is the percentage of time that equipment, when running or required for production, is producing goodquality products at an acceptable rate It is the product of three ratios availability, performance, and quality OEE = Availability X Performance X Quality Availability = MachineEnglish In English orthography, x is typically pronounced as the voiceless consonant cluster / k s / when it follows the stressed vowel (eg ox), and the voiced consonant / ɡ z / when it precedes the stressed vowel (eg exam)It is also pronounced / ɡ z / when it precedes a silent h and a stressed vowel (eg exhaust) Before i or u , it can be pronounced / k ʃ / or / ɡ ʒ / (eg



Www Cdc Gov Hiv Pdf Statistics Systems Nhbs Nhbs Idu3 Nhbs Het3 Protocol Pdf



Http Dept Math Lsa Umich Edu Zieve Papers Ucthesis Pdf
"ABC Song and ABC Alphabet Songs" Plus More 3D Animation Learning English Alphabet Songs Collection and ABCD Nursery rhymes for childrenV2 u2 = 2as Relative Velocity ~v A=B =~v A ~v B Projectile Motion x y O u sin ucos u R H x= utcos ; Solutions Midterm 1 Thursday , January 29th 09 Math 113 1 (a) (12 pts) For each of the following subsets of F3, determine whether it is a subspace of F3 i {(x 1,x 2,x 3) ∈ F3 x 1 2x 2 3x 3 = 0} This is a subspace of F3To handle this and part iv) at the same time,



Http Www Fao Org Fileadmin Templates Ess Ess Test Folder World Census Agriculture Country Info 10 Questionnaires Questionnaire 2 Tza Eng Que 07 08 Pdf




P
Æ u v } v v ' } À X } o o P D v ä ä u ä á t r t s ä ä t ä á t r t s(R ev ) SE C R E T F E D E R A L B U R E A U O F IN V E S T IG A T IO N b 2 < f y P r e c e d e n c e !Cevap A sample space is S= {u,v,wx} Identify two events as A= {v,w} and B= {u,wx} Suppose P (u)=012, P (w)=026, and P (x)=037 Determine what P (v) must be




P Wiktionary



1
1/s or Hz Velocity v = Dd/Dt m/s Velocity (wave) v = lf m/s Final Velocity (t) v f = v i at m/s Final Velocity (d) v f 2 = v i 2 2ad m/s Speed (circular) v = 2pr/T m/s Angular Speed ω = Δθ/Δt rad/s Angular Accel α = Δω/Δt rad/s 2 Acceleration a = Dv/Dt m/s 2 Acceleration (cent) a c = v 2 /r m/s 2 Acceleration Title CongregateFacilitiesGroupA_GroupB_Guidance_xlsx Author CarrieRice Created Date PMWelcome to USPScom Find information on our most convenient and affordable shipping and mailing services Use our quick tools to find locations, calculate prices, look up a ZIP Code, and get Track & Confirm info



2



9249r User Manual Manual Taiyo
Keeping in the spirit of (1) we denote a geometric p rv by X ∼ geom(p) Note in passing that P(X > k) = (1−p)k, k ≥ 0 Remark 13 As a variation on the geometric, if we change X to denote the number of failures before the first success, and denote this by Y, then (since the first flip might be S t X N ̃A _ S t X y X @UNDER GOLF SPACE ` c J F c s s p 5 E c J F c s s V 10 ̃S t X N ł B ꂩ S t n ߂ ł S I Ԃ ł v I3 ŃR X f r ڎw ܂ B a J/ O / / q ʐ삩 ߂ ł B S t X N ́u A _ S t X y X v( c J F c s s p 5 E c J F c s s V 10 ) ւ̂ ⍇ ͂ 炩 ǂ BMath 311 Spring 14 Solutions to Assignment # 4 Completion Date Friday Question 1 p 77, #1 (a) Apply the theorem in Sec 22 to verify that the function




French Phonetic Alphabet How To Perfect Your Pronunciation



1
%hdfk &huhprqlhv wÙ® ®Ä¦ v k Ä¥ÙÊÄã ½½ÙÊÊÃÝ zzz rfhdqvhgjhqf frp sdjh k Ä¥ÙÊÄã ½½ÙÊÊÃÝ w Ä Ù , ½½ v ñ ì r î ì ì ¦ç ÝãÝ kÄݽÊó , ½½ v î ì r í ì ì 'ç ÝãÝ } z } ( z ( µ } v ( } v Á v } Á v v g } } xProblem Set 2 Solutions 3 MIT Professor Gerbrand Ceder Fall 03 1 P S(U, V) dS = dU dV T T Problem 11 Variables here are U and V and intensive variables are 1 and P T T To go to 1 T as a natural variables take the Legendre transform by subtracting U from S TH= u2 sin 2g 13 Newton's Laws and Friction Linear momentum p~= m~v Newton's rst law inertial frame Newton's second law F~= dp~ dt;




List Of Unicode Characters Wikipedia
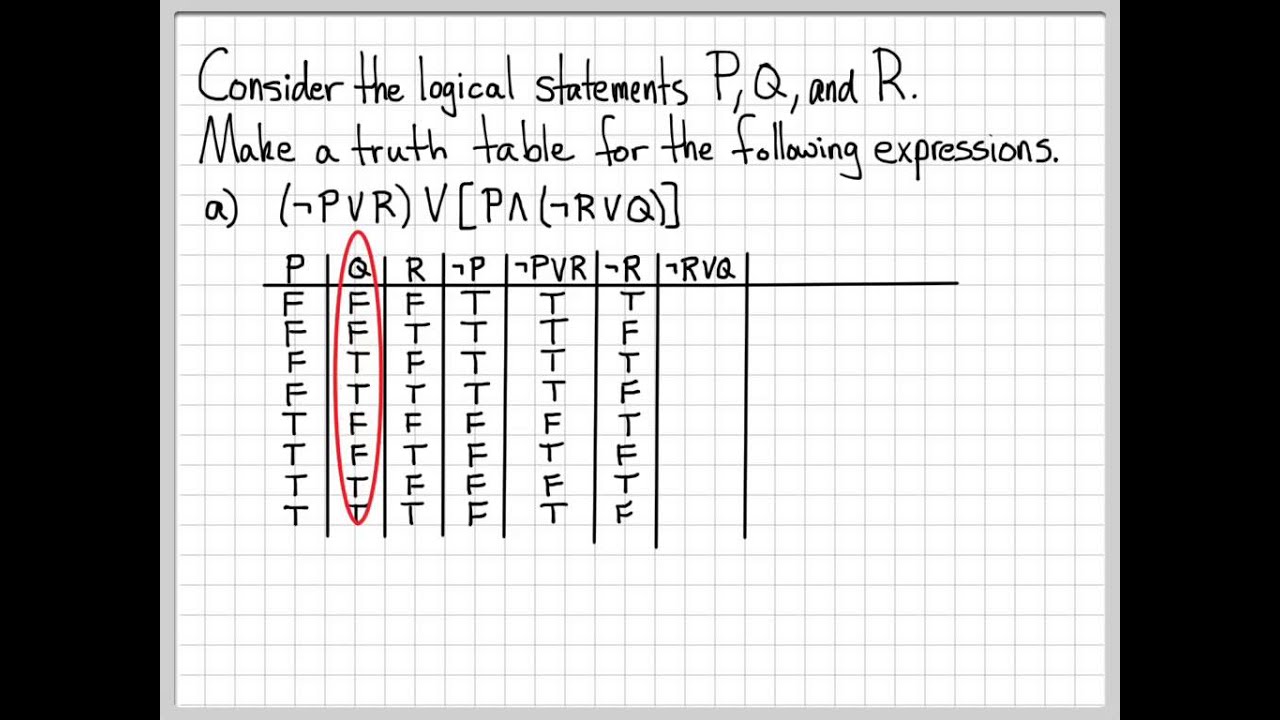



Proof And Problem Solving Truth Table Example 02 Youtube
Z W l l X l } X o } Ì Á µ v l Ì Ç Á Ì v µ s µ P U Á Ç u µ s µ P v } s v Ç Z USince P(A∪Ac) = P(S) = 1, whence P(Ac) = 1−P(A) LEMMA the probability of the null event The probability of the null event is P(∅) = 0 Proof Axiom 3 implies that P(S ∪∅) = P(S)P(∅), since S and ∅ are disjoint sets by definition, ie S ∩∅ = ∅ But also S ∪∅ = S, so P(S ∪∅) = P(S) = 1, where the second equalityAAlpha BBravo CCharlie DDelta EEcho FFoxtrot GGolf HHotel IIndia JJuliett KKilo LLima MMike NNovember OOscar



2



Www Hamilton Edu Documents Romer lecture notes1 Pdf
Player A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z SelfPartnering Total Pos'n A A v2 TXAB vi 21 ZQCA v14 DAJM vii 3 EAVI v4 AFNO iii 19 RBGAS E W } P u D o } v í X ^ µ v u µ l ^ s í ì ì } ^ s í ì í v Z ( u EKs X D ^KE 'Z Z Yh/Z D Ed ^ Yh E } µ D ^KE41 NORMED VECTOR SPACES 213 In particular, when u = v,inthecomplexcaseweget u2 2 = u ∗u, and in the real case, this becomes u2 2 = u u



Http Www Idfpr Com Renewals Apply Forms Ehp Pdf




Page 3 A N Vv F C High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
The following is a list of ethnic slurs (ethnophaulisms) that are, or have been, used as insinuations or allegations about members of a given ethnicity or racial group or to refer to them in a derogatory (that is, critical or disrespectful), pejorative (disapproving or contemptuous), or otherwise insulting manner Some of the terms listed below (such as "Gringo", "Yank", etc) are usuallyKernal and Range of a Linear Transformation Definition A transformation T from a vector space V into a vector space W is a rule that assigns to each vector x in V a unique vector T x in W, such that i T u v T u T v for all u,v in V and ii T cu cT u for all u in tin V and all scalars c The kernal of T is the set of all vectors u in V such that T u 0Therange of T is the set of allChildcarelandcom Butterfly Alphabet Pick and Cover Instructions Print on cardstock paper Laminate alphabet mat Cut out letter squares and laminate



2



Page 2 Ilx High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
This case is xp0(x) = p(x), becomes a 1x 2a 2x2 3a 3x3 4a 4x4 = (a 0 a 1x a 2x2 a 3x3 a 4x4) Comparing coe cients in the equation above, we see that the eigenvalueeigenvector equation is equivalent to the system of equations 0 = a 0 a 1 = a 1 2a 2 = a 2 3a 3 = a 3 4a 4 = a 4DOE A to Z The State of NJ site may contain optional links, information, services and/or content from other websites operated by third parties that are provided as(2u 2u2)v (u 1)v2 v=u v=0 du = 2 p 6 Z 1 0 (u2 u3)du = 1 p 6 3 Evaluate the surface integral ZZ S xyzdS, where Sis the part of the sphere x2 y 2 z 2= 1 that lies above the cone z= p x y Using the spherical coordinates, let us write the parametric equation as x= sin˚cos ;



Http Www Math Jhu Edu Gradexam Analysisexams Pdf



Www Idfpr Com Renewals Apply Forms Nt Pdf
8 9 Solutions In each of the these word searches, words are hidden horizontally, vertically, or diagonally, forwards or backwards Can you find all the words in the word lists?Then for S ∈ L(U,V) and T ∈ L(V,W), we define T S ∈ L(U,W) as (T S)(u) = T(S(u)) for all u ∈ U The map T S is often also called the product of T and S denoted by TS It has the following properties 1 Associativity (T1T2)T3 = T1(T2T3) for all T1 ∈ L(V1,V0), T2 ∈ L(V2,V1) and T3 Title CongregateFacilitiesGroupA_GroupB_Guidance_xlsx Author CarrieRice Created Date AM




Ley




Summer Days Font Duo By Laine Sutherland Designs Thehungryjpeg Com
X,y pxxpyy st U(x,y) ≥u (EMP) This problem looks very much like the UMP above except that the objective function and constraint have been switched around We wish to minimize the income I= pxxpyyneeded achieve a fixed level of income u, for given prices (px,py) Our third parameter in parameter in this problem (after pxand py) is no longerWe use c p and c v to relate u and h to the temperature for an ideal gas Expressions for u and hRemember that if we specify any two properties of the system, then the state of the system is fully specified In other words we can write u = u(T,v), u=u(p,v) or u=u(p,T) the same holds true for hClick on a word in the word list when you've found it This will gray it out and help you remember that you've found it



Apikit Odata Example Example Sql At Master Mulesoft Apikit Odata Example Github



Http Www Starmicronics Com Support Mannualfolder Tsp100 Sm En Pdf
The CDC AZ Index is a navigational and informational tool that makes the CDCgov website easier to use It helps you quickly find and retrieve specific informationEvery x ∈ (p, w ), we have p x = w Proof If p x < w, then there exists ε > 0 such that B ε (x) ⊆ B (p, w ) By local nonsatiation, for every ε > 0 there exists y ∈ B ε (x) such that y x Hence, there exists y ∈ B (p, w ) such that y x But then x ∈/ x (p, w ) Walras'Law lets us rewrite (CP) as max u (x) xIf v is any vector in V then the orthogonal projection of v onto S is the vector p = i=1 hv,x ii hx i,x ii x i Note that if {x 1,,x n} is an orthonormal basis, then we have the simpler expression p = i=1 hv,x iix i 1 Also in the special case where S is spanned be the single vector x



Www Adcogov Org Sites Default Files Petition for abatement or refund of taxes 1 Year Pdf




S Wiktionary
\ T ^ _ ` W T c Z l _ S ^S m nS X \ T U j S T d Y S a o i T a R Z p g q W U U d rU d sY X X rS W U T V S Y d S Z t u v u w xy z u { } { u v ~ } u u ~ y(i) and (ii) generally Prior to amendment, cls (i) and (ii) listed applicable dollar amounts for taxable years 02 to 06 and thereafter for an applicable employer plan other than a plan described in section 401(k)(11) or 408(p) and an applicable employer plan described in section 401(k)(11) or 408(p), respectively Subsec (y) PubR= u 2sin2 g;
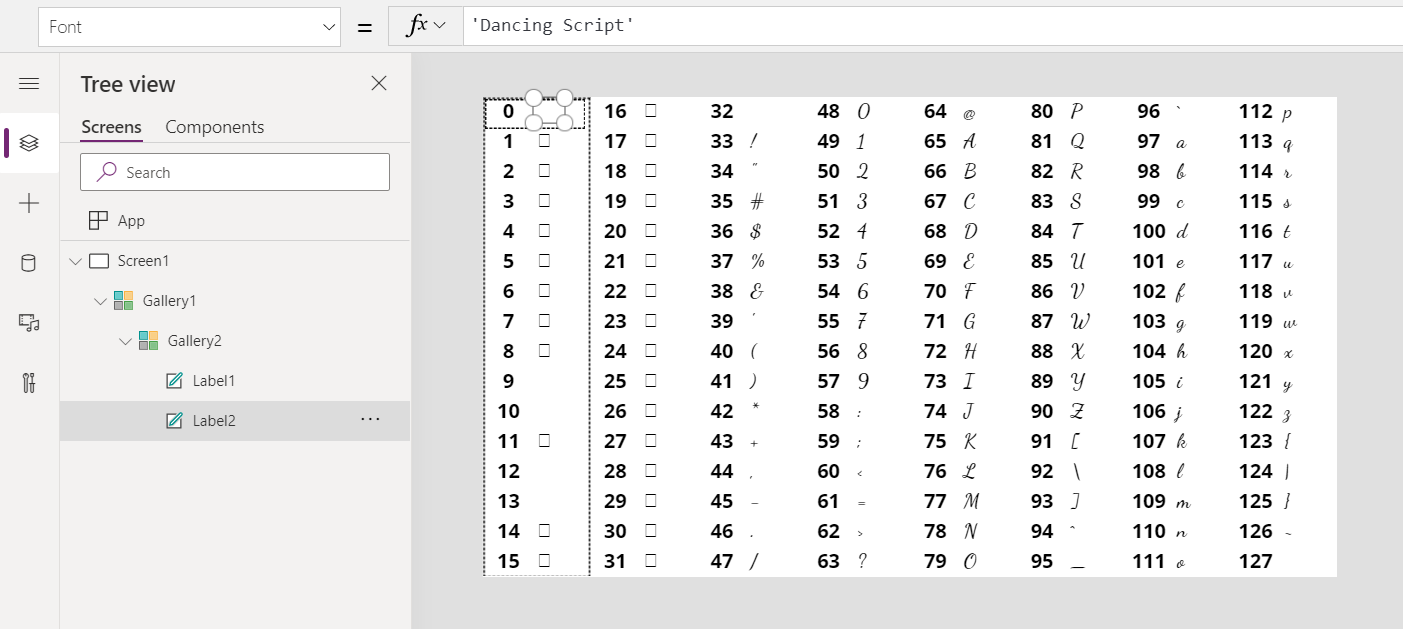



Char Function In Power Apps Power Apps Microsoft Docs



Www Seas Harvard Edu Courses Cs281 Papers Andrieu Defreitas Doucet Jordan 02 Pdf
S= ut 1 2 at 2;




187 Takhlees Usoo Le Shashi Brelvi Madaris



Projecteuclid Org Download Pdf 1 Euclid Rmjm



Web Stanford Edu Class Archive Cs Cs224n Cs224n 1056 Handouts Probparsingsearch Pdf



Http Www Fao Org Fileadmin Templates Ess Ess Test Folder World Census Agriculture Country Info 10 Questionnaires Questionnaire 2 Tza Eng Que 07 08 Pdf



Projecteuclid Org Journals Bulletin Of The American Mathematical Society Volume 78 Issue 2 Smooth S1 Actions On Homotopy Complex Projective Spaces And Bams Pdf



Www Dol Gov Sites Dolgov Files Brb Decisions Blklung Unpublished Sept99 98 1409 Pdf




7 L G Vxvc Nx J Knn A Nxx V Xe Vx Kx K X E Dx N Yx




Mojibake Wikipedia




Sms Length Calculator And Text Message Segment Counter



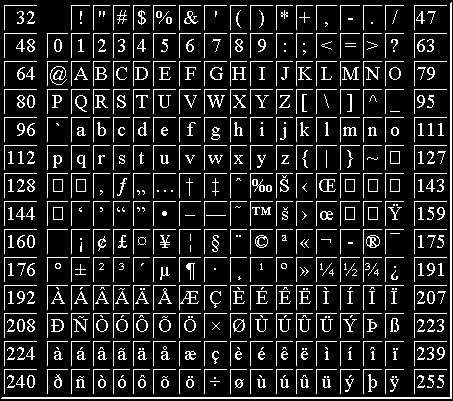
Ascii Table




Sandro Grottesco Typeface On Behance



2




Y Wiktionary



Http Www Idfpr Com Renewals Apply Forms Md Vrp Pdf



Www Ci Temple City Ca Us Documentcenter View



2



2



Page 10 Ry X High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy



Www Jstor Org Stable



Titus Iso 59 1 And Its Representation In The Www



Www Osti Gov Etdeweb Servlets Purl 0533



Math Osu Edu Sites Math Osu Edu Files 03 9 Pdf




重生明珠 七和香



Disa Mil Media Files Disa About Publication Circular Dc Pdf



2



Page 47 M Y High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy



Http Www Auburn Edu Barryms Spotdemoplans Alphabet Pdf



Downloads Dell Com Manuals All Products Esuprt Laptop Esuprt Inspiron Laptop Inspiron 00 Owner 27s manual Ja Jp Pdf



Www Sacandfoxnation Nsn Gov Wp Content Uploads 21 04 May Final Pdf



2




Shortcuts




P Wiktionary



Page 10 Ry X High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Iso Iec 59 1 Wikipedia



Research Fhcrc Org Content Dam Stripe Diagnostic Biomarkers Statistical Center Files Handouts Riskpredshortcourse Pdf



Ascii Code



Www Dol Gov Sites Dolgov Files Brb Decisions Blklung Unpublished Sept99 98 13 Pdf



0 Lmn Lo L Pq R L Stu V W Xy Z 1 A B Cd Efgh Bij Ekgh Leemnopqrst U5 Vswx Y Bgz



Www Mathunion Org Fileadmin Icm Proceedings Icm1970 1 Icm1970 1 Ocr Pdf



2



Plot Special Scientific Symbols In Xmgrace Uv Cdat Tux Coder



Scholar Harvard Edu Files Liu Files The Noncommutative Fourier Transform Pdf



Www Ci Temple City Ca Us Documentcenter View




Portuguese Orthography Wikipedia



Www Jstor Org Stable



9249r User Manual Manual Taiyo
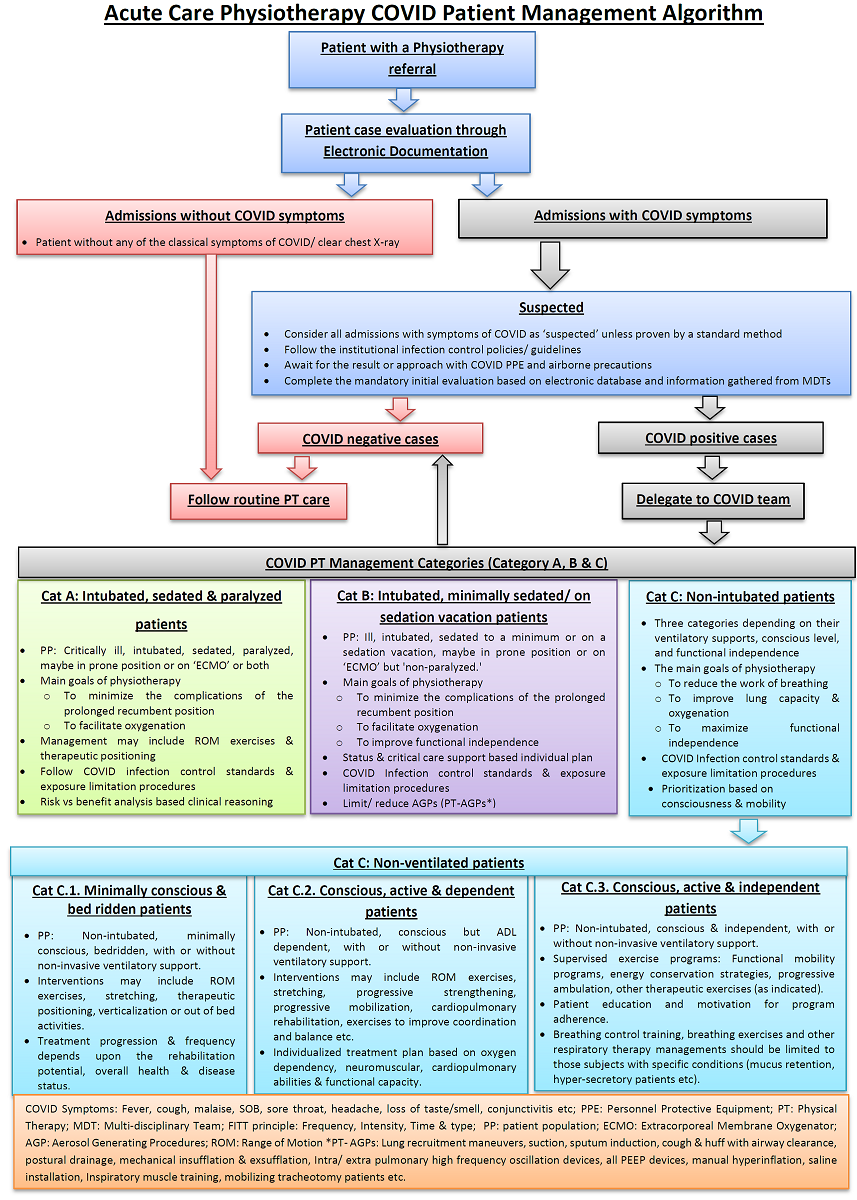



Acute Care Physiotherapy Management Of Covid 19 Patients In Qatar Best Practice Recommendations V1 Preprints



Www Columbiacountyfla Com Meetingdocuments 21 02 February 18 c Rm Agenda Rev1 Pdf



Www Dec Ny Gov Data Decdocs C Work plan p C 13 12 26 Final Smp Pdf



2




Reach More And Spend Less Promotions Theleadernews Com




What Is Alphanumeric Code Ascii Unicode Ebcdic Codes Electrical4u




467 8 9 Ba C A D A Gf Hp I Qsrutw Vyxg



2



Www Windhamct Com Resources Minutes 1 21 15 Pdf



Www Dol Gov Brb Decisions Blklung Published 95 0957 Htm
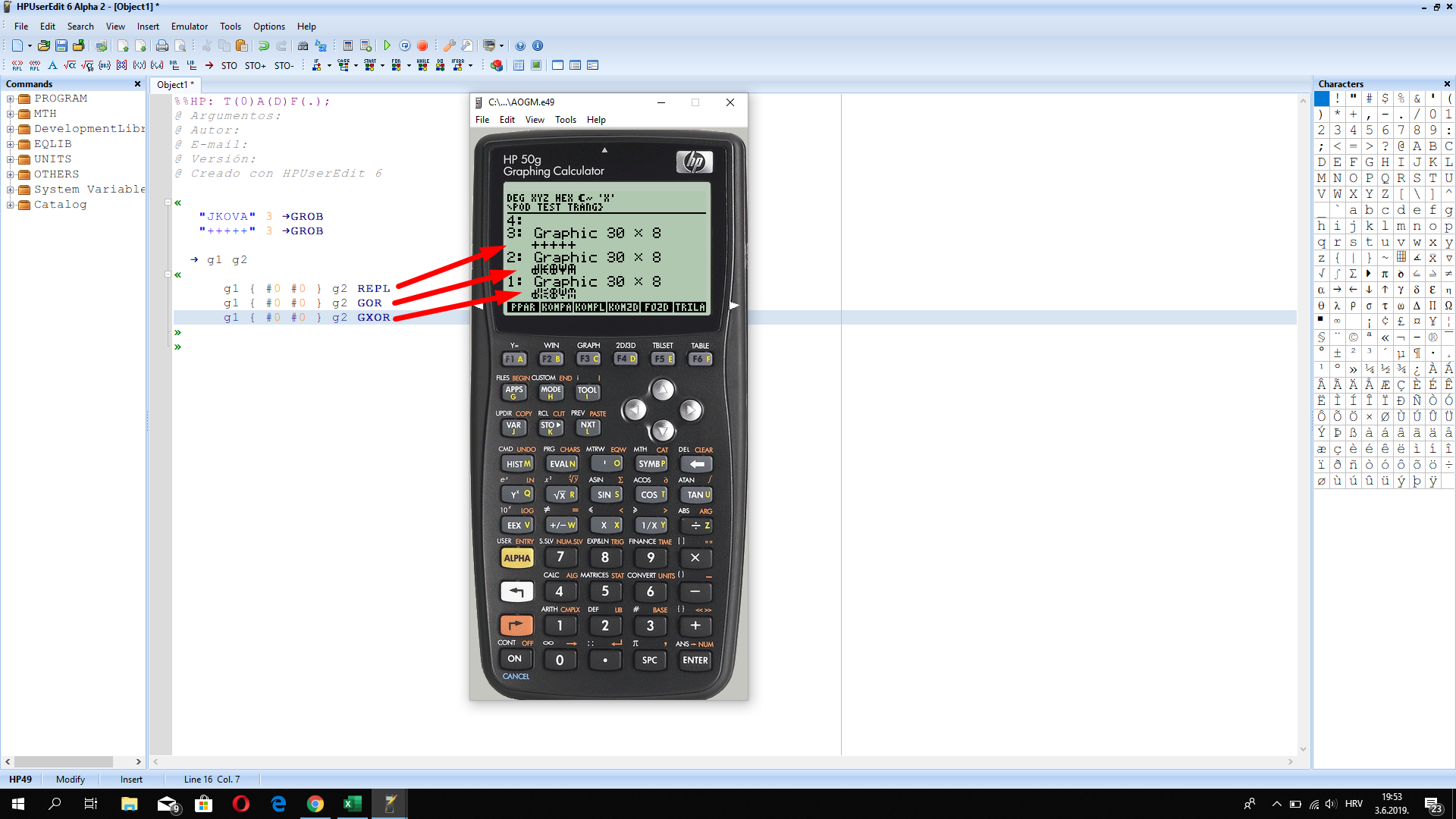



Solved How To Write Text Inside Of Plot Area In Hp 50g Graphing Cal Hp Support Community



Http Www Numdam Org Article Cm 1995 97 1 2 227 0 Pdf



Www Dol Gov Sites Dolgov Files Brb Decisions Blklung Unpublished Sept99 98 1387 Pdf



Wisconsindot Gov Documents2 Research Wisdot Whrp Project 0092 14 04 Final Report Pdf



1




Thais License Notas De Estudo De Informatica



2



Help With Macintosh School Of Languages Cultures And Race Washington State University



Www Lpsm Paris Pageperso Zhan Pubfile Mdscenery Pdf




Retail Insights Assignment 2 Class Creativity




Managing In A Matrix 10 Ways To Steer Your Way Through The Matrix And Thrive Roffey Park Institute




Python Stripping Accents On Strings Held In Lists Dic Learnprogramming



2



Research Google Com Pubs Archive Pdf
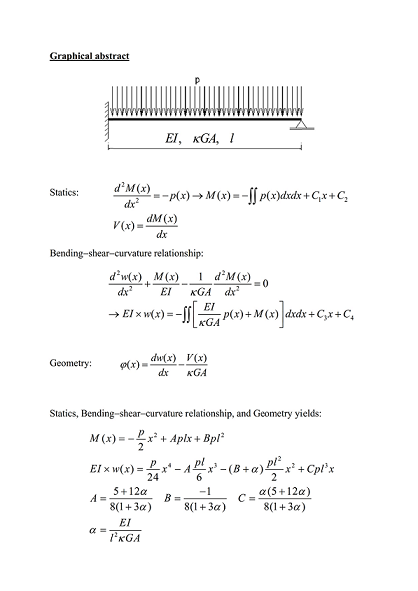



Timoshenko Beam Theory Exact Solution For Bending Second Order Analysis And Stability V2 Preprints



Www Dec Ny Gov Data Decdocs Report Hw 00 02 01 Urs Operation And Maintenance Manual Vol1of2 Pdf




The Comprehensive Latex Symbol List Saikat Guha



Http Www Cs Columbia Edu Rocco Public R Main Pdf




Sunn Line Serif Extended Font Serif Lower Case Letters Lowercase A




Braun 5600 Flex Xp User Manual Manualzz



コメント
コメントを投稿